React 19.2
October 1, 2025 by The React Team
React 19.2 is now available on npm!
This is our third release in the last year, following React 19 in December and React 19.1 in June. In this post, we’ll give an overview of the new features in React 19.2, and highlight some notable changes.
New Features
<Activity />
<Activity> lets you break your app into “activities” that can be controlled and prioritized.
You can use Activity as an alternative to conditionally rendering parts of your app:
// Before
{isVisible && <Page />}
// After
<Activity mode={isVisible ? 'visible' : 'hidden'}>
<Page />
</Activity>In React 19.2, Activity supports two modes: visible and hidden.
hidden: hides the children, unmounts effects, and defers all updates until React has nothing left to work on.visible: shows the children, mounts effects, and allows updates to be processed normally.
This means you can pre-render and keep rendering hidden parts of the app without impacting the performance of anything visible on screen.
You can use Activity to render hidden parts of the app that a user is likely to navigate to next, or to save the state of parts the user navigates away from. This helps make navigations quicker by loading data, css, and images in the background, and allows back navigations to maintain state such as input fields.
In the future, we plan to add more modes to Activity for different use cases.
For examples on how to use Activity, check out the Activity docs.
React Performance Tracks
React 19.2 adds a new set of custom tracks to Chrome DevTools performance profiles to provide more information about the performance of your React app.
Scheduler ⚛
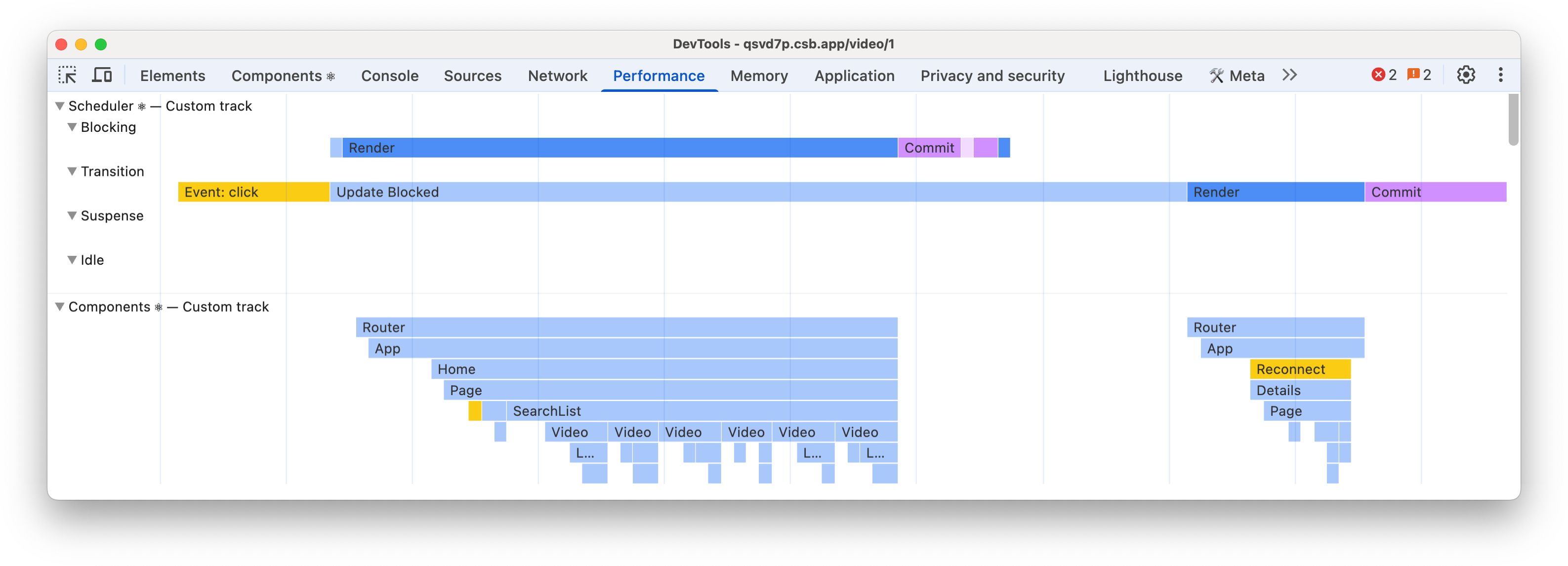
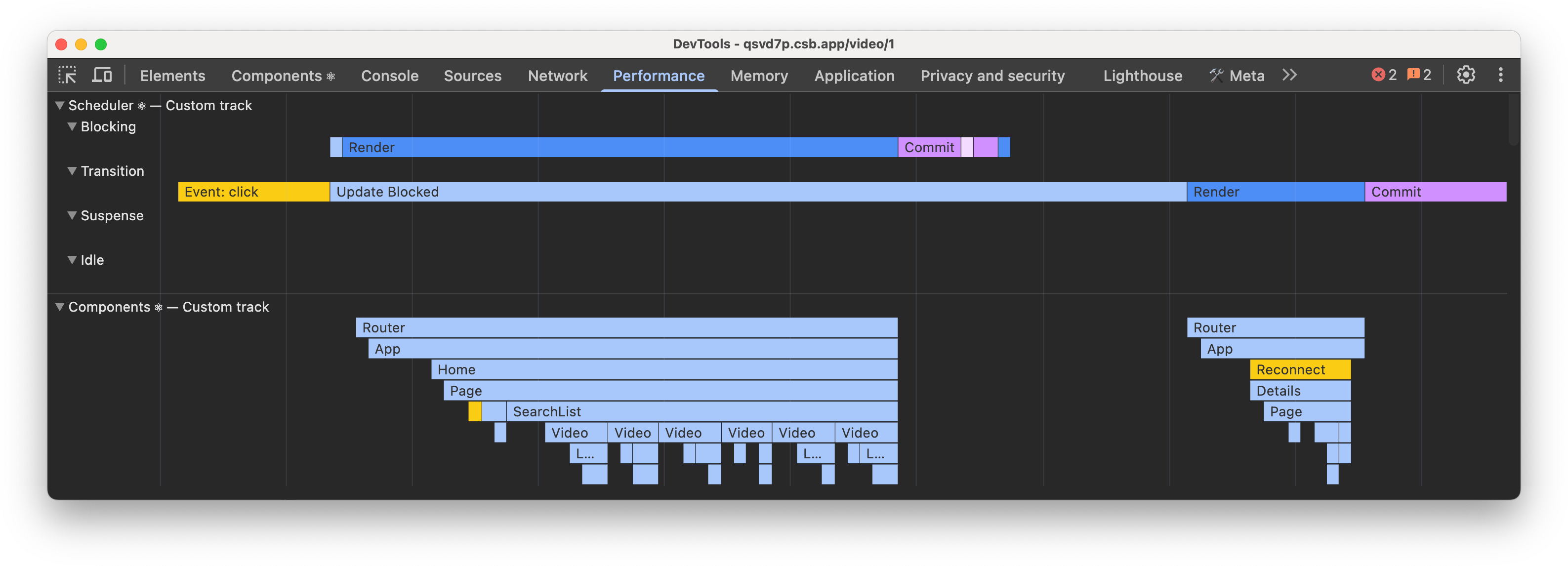
The Scheduler track shows what React is working on for different priorities:
- Blocking - synchronous updates such as user interactions.
- Transition - non-blocking updates such as Actions, or useDeferredValue.
- Suspense - non-blocking updates rendering of Suspense content.
- Idle - non-blocking updates such as children hidden by Activity.
Inside each track, you will see the type of work being performed such as:
- Event - the event that triggered an update.
- Update - this is what scheduled an update.
- Render - rendering components (visible in the Components track).
- Commit - committing the changes to the UI, and running effects during commit such as useLayoutEffect.
- Remaining Effects - running effects after commit, such as useEffect.
You’ll also see states of work, such as:
- Update Blocked - when an update is waiting for a different priority of work.
- Waiting for Paint - when React yields for paint before continuing work such as running effects.
See the Scheduler track docs for a full list.
Components ⚛
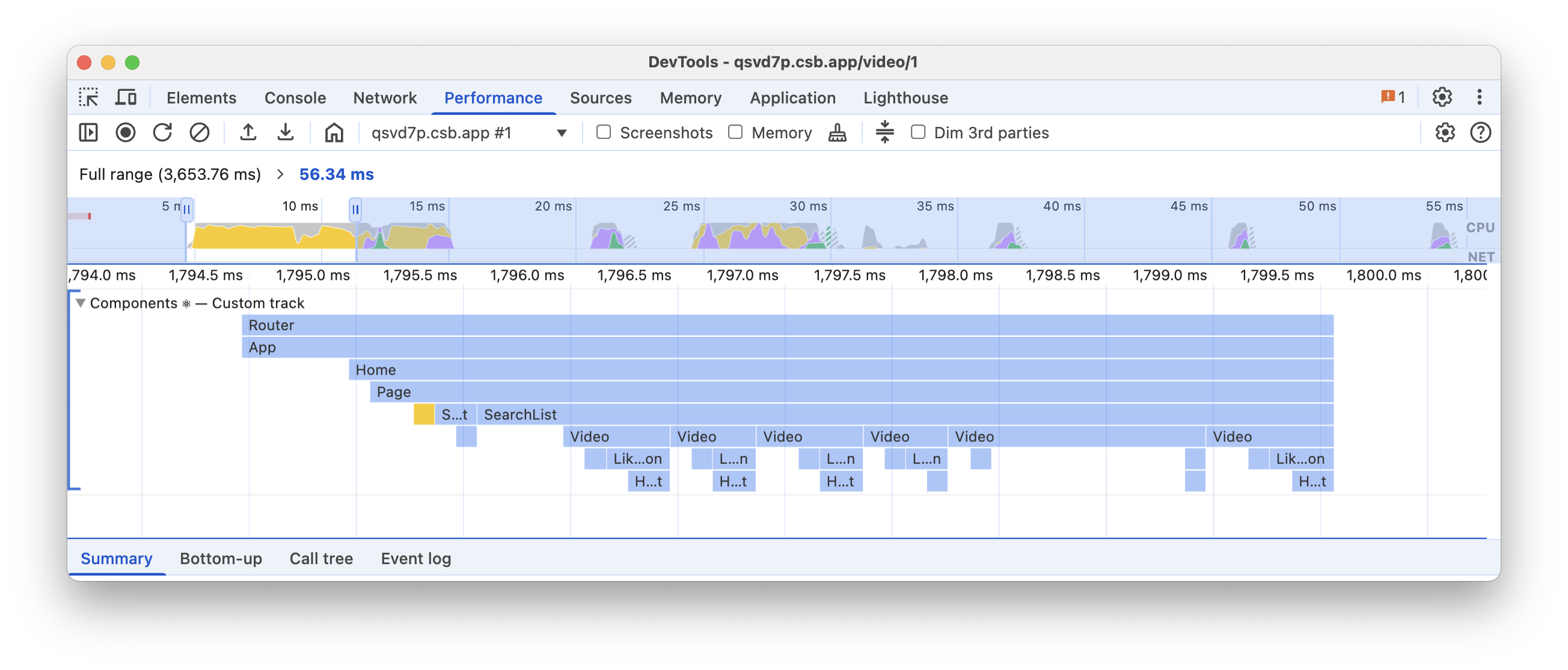
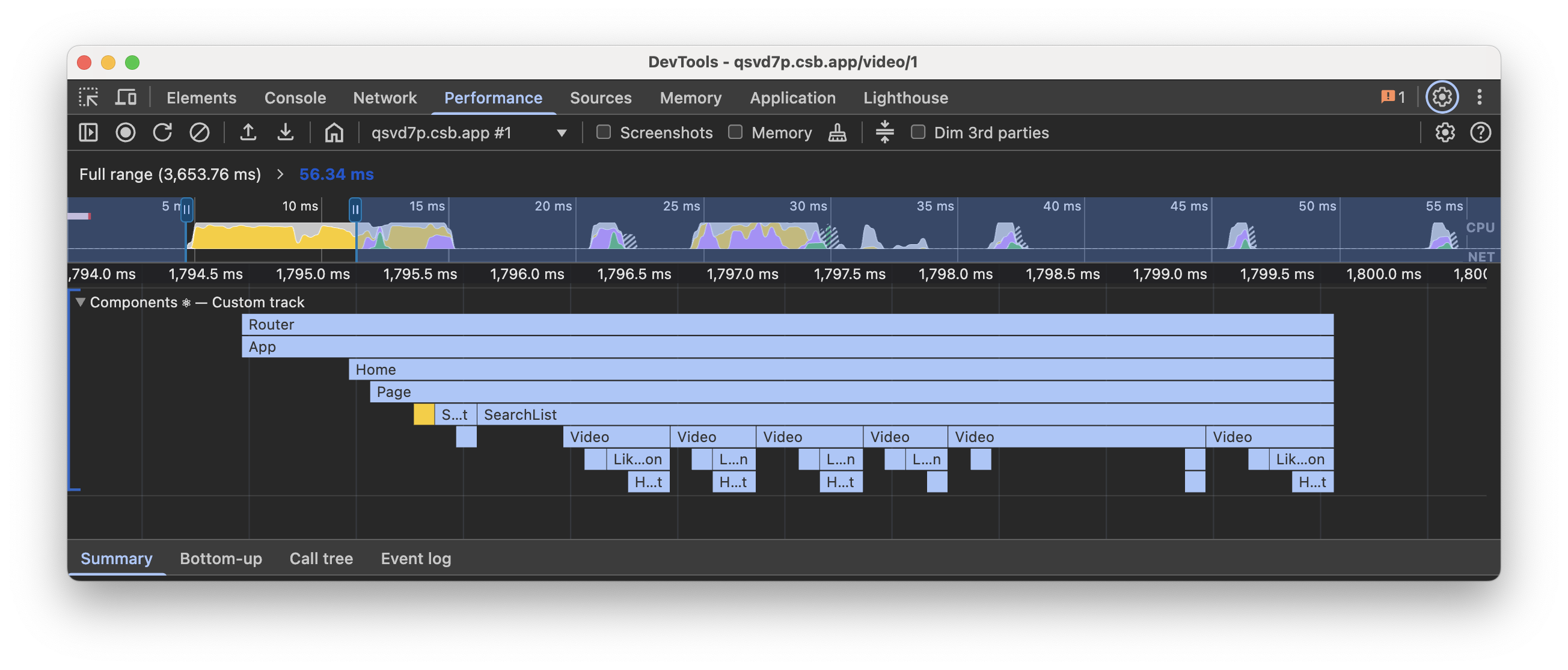
The Components track shows the tree of components that React is working on either to render or run effects.
You’ll see labels such as:
- Mount - When the children mount or effects are mounted.
- Unmount - When the children unmount or effects are unmounted.
- Reconnect - Similar to Mount, but for
<Activity>. - Disconnect - Similar to Unmount, but for
<Activity>. - Blocked - When rendering is blocked due to yielding to work outside React.
Each entry represents the duration of the corresponding component render and all its descendant children components. For each component, the color of the bar indicates how long the component itself took:
- 0-0.5ms: light
- 0.5-10ms: darker
- 10ms-100ms: darkest
- > 100ms: red
See the Component track docs for a full list.
Finding performance issues
Finally, the performance tracks include information to help identify performance pitfalls. For example, setting state in an Effect creates a “Cascading update”, which is a common patterns for performance regressions.
React flags cascading renders in the performance tracks and marks them with a red Cascading Update label:
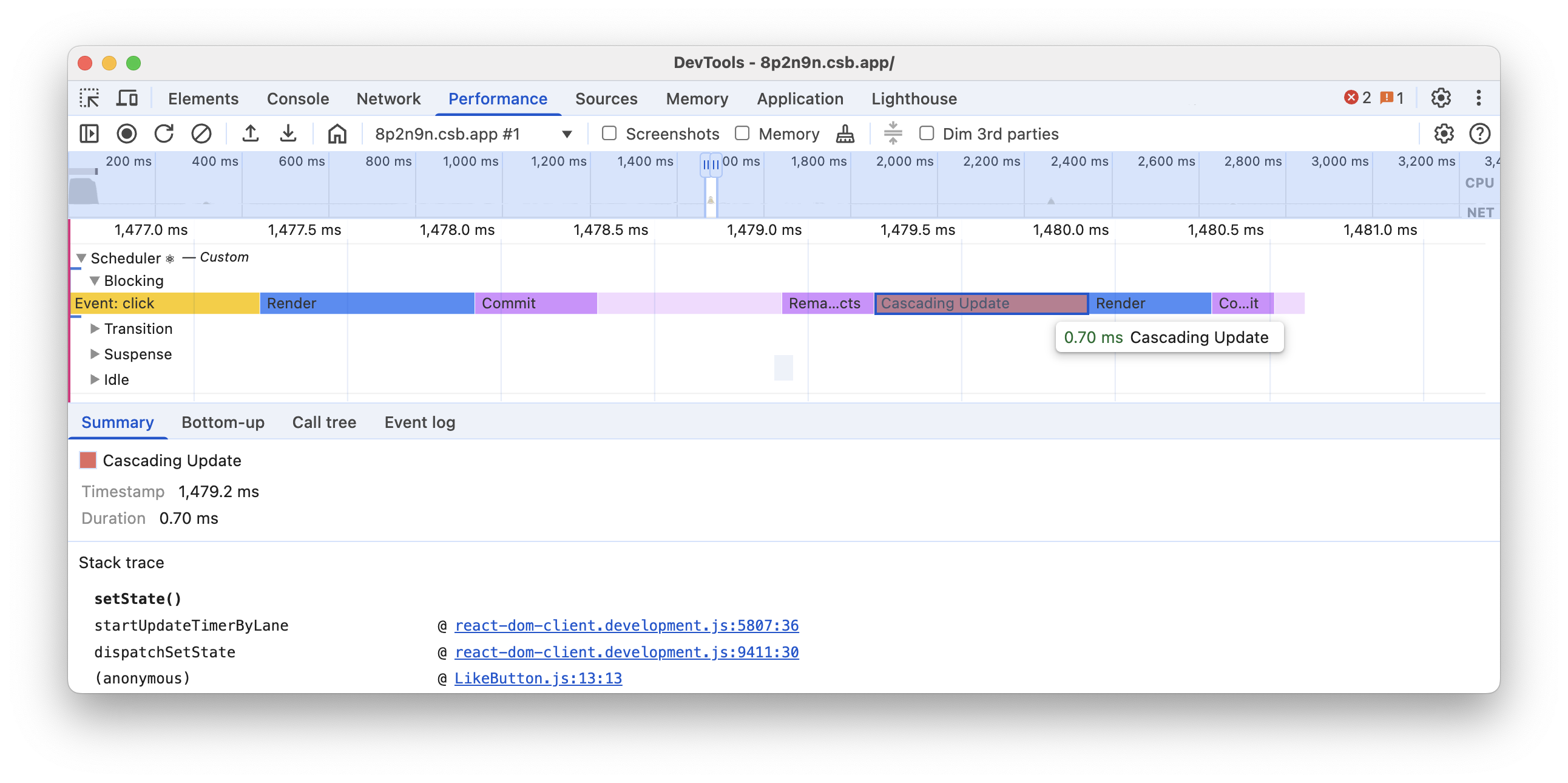
These performance tracks are just a start. We will continue to expand on the performance tracks to provide more information and insights about your app.
For more information, see the React Performance Tracks docs.
useEffectEvent
When using Effects you may want to read the most recent props or state inside an Effect without re-running the Effect when those values change. For example, in the following code the theme prop is used inside an Effect, but we don’t want the Effect to re-run when theme changes:
function ChatRoom({ roomId, theme }) {
useEffect(() => {
const connection = createConnection(serverUrl, roomId);
connection.on('connected', () => {
showNotification('Connected!', theme);
});
connection.connect();
return () => {
connection.disconnect()
};
}, [roomId, theme]);
// ...To solve this, most users just disable the lint rule and exclude the dependency. But that can lead to bugs since the linter can no longer help you keep the dependencies up to date if you need to update the Effect later.
React 19.2 introduces useEffectEvent, which lets you declare “Effect Events” that can be called inside Effects. Effect Events always access the latest values from props and state when they are invoked, so you can read the latest values without re-running the Effect:
With useEffectEvent, we can define the onConnected callback as an “Effect Event”. Now, it doesn’t re-run when the values change, but it can still “see” the latest values of your props and state:
function ChatRoom({ roomId, theme, threadId }) {
const onConnected = useEffectEvent(() => {
showNotification('Connected!', theme);
});
useEffect(() => {
const connection = createConnection(serverUrl, roomId, threadId);
connection.on('connected', () => {
onConnected();
});
connection.connect();
return () => connection.disconnect();
}, [roomId, threadId]); // ✅ All dependencies declared
// ...For more information, see Separating Events from Effects and the useEffectEvent docs.
cacheSignal
cacheSignal allows you to know when the cache() lifetime is over:
import {cache, cacheSignal} from 'react';
const dedupedFetch = cache(fetch);
async function Component() {
await dedupedFetch(url, { signal: cacheSignal() });
}This allows you to clean up or abort work when the result will no longer be used in the cache, such as:
- React has successfully completed rendering
- The render was aborted
- The render has failed
For more info, see the cacheSignal docs.
Notable Changes
Batching Suspense Boundaries for SSR
We fixed a behavioral bug where Suspense boundaries would reveal differently depending on if they were rendered on the client or when streaming from server-side rendering.
Starting in 19.2, React will batch reveals of server-rendered Suspense boundaries for a short time, to allow more content to be revealed together and align with the client-rendered behavior.


Previously, during streaming server-side rendering, suspense content would immediately replace fallbacks.


In React 19.2, suspense boundaries are batched for a small amount of time, to allow revealing more content together.
This fix also prepares apps for supporting <ViewTransition> for Suspense during SSR. By revealing more content together, animations can run in larger batches of content, and avoid chaining animations of content that stream in close together.
SSR: Web Streams support for Node
React 19.2 adds support for Web Streams for streaming SSR in Node.js:
renderToReadableStreamis now available for Node.jsprerenderis now available for Node.js
Update the default useId prefix
In 19.2, we’re updating the default useId prefix from :r: (19.0.0) or «r» (19.1.0) to _r_.
The original intent of using a special character that was not valid for CSS selectors was that it would be unlikely to collide with IDs written by users. However, to support View Transitions, we need to ensure that IDs generated by useId are valid for view-transition-name and XML 1.0 names.
Changelog
Other notable changes
react-dom: Allow nonce to be used on hoistable styles #32461react-dom: Warn for using a React owned node as a Container if it also has text content #32774
Notable bug fixes
react: Stringify context as “SomeContext” instead of “SomeContext.Provider” #33507react: Fix infinite useDeferredValue loop in popstate event #32821react: Fix a bug when an initial value was passed to useDeferredValue #34376react: Fix a crash when submitting forms with Client Actions #33055react: Hide/unhide the content of dehydrated suspense boundaries if they resuspend #32900react: Avoid stack overflow on wide trees during Hot Reload #34145react: Improve component stacks in various places #33629, #33724, #32735, #33723react: Fix a bug with React.use inside React.lazy-ed Component #33941react-dom: Stop warning when ARIA 1.3 attributes are used #34264react-dom: Fix a bug with deeply nested Suspense inside Suspense fallbacks #33467react-dom: Avoid hanging when suspending after aborting while rendering #34192
For a full list of changes, please see the Changelog.
Thanks to Ricky Hanlon for writing this post, Dan Abramov, Matt Carroll, Jack Pope, and Joe Savona for reviewing this post.